test for testicular torsion ultrasound|testicular torsion treatment guidelines : tv shopping Ultrasound is the modality of choice for evaluating the potentially torsed testis. It is simultaneously able to assess the structure of the testis . See more WEB11 de abr. de 2023 · Reclame com a ajuda da PROTESTE; Reclamações públicas; Título da reclamação pública Voltar Mercadoria não entregue/ Sem retorno da empresa . No dia 13/02/2023 fiz uma compra no site Lado Fit no valor de R$ 192,97 no ato da compra a informação era que o prazo de entrega era de 11 dias uteis. Informaram que o prazo de .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Atletico Madrid 0, Villarreal 2. Gerard Moreno (Villarreal) left footed shot from the left side of the box to the bottom right corner. Assisted by Alfonso Pedraza following a fast break.
Anatomically there are two types of testicular torsion which occur in different age groups 2,3: 1. extra-vaginal (supravaginal) 1.1. torsion occurs at the level of the external inguinal ring 1.2. seen in neonates 2. intra-vaginal 2.1. more common variety due to bell clapper deformity(see below) 2.2. typically occurs in . See moreThe majority of cases of testicular torsion are either spontaneous or in the setting of minor/incidental trauma. In approximately 5-8% of cases, . See more
Ultrasound is the modality of choice for evaluating the potentially torsed testis. It is simultaneously able to assess the structure of the testis . See moreIn the neonatal form of torsion (extravaginal or supravaginal) the whole content of the hemiscrotum rotates around the spermatic cord at . See moreThe key to successful treatment is rapid diagnosis and surgical intervention. If diagnosed early enough, the testis can be detorted with little damage. If the testis has necrosed, then orchiectomy is required. Likelihood of salvage of the testis is directly related to the . See more Testicular torsion is a true urologic emergency, and early identification is critical to prevent the need for testicular amputation. Ultrasound is the ideal imaging modality to .
Testicular torsion is a clinical diagnosis, and patients typically present with severe acute unilateral scrotal pain, nausea, and vomiting. Physical examination may reveal a high-riding.
Normally, this reflex causes the testicle to contract and rise, but it is often absent in individuals with testicular torsion. Additional tests that may be performed include urine analysis, as well as ultrasound imaging of the . A testicular ultrasound is a noninvasive imaging test. Healthcare providers use it to diagnose and treat conditions that affect your testicles and surrounding areas. . A testicular ultrasound is an imaging test that uses high-frequency sound waves to take images (sonograms) of your testicles and the surrounding tissues in your groin area .
Testicular torsion is a challenging and time-sensitive diagnosis that is encountered frequently in daily practice, especially in the emergency room. . in incomplete torsion, Doppler ultrasound is known to have a high false-negative rate. 29 Conventional color Doppler ultrasonography can also lead to a misdiagnosis as it only assesses the .
A testicular ultrasound is a low-risk procedure for diagnosing a range of medical issues, such as testicular torsion, testicular cancer, and epididymitis.
Scintigraphy may still play a role when testicular torsion has not been ruled out and US is inconclusive. Near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) NIRS has been proposed as a potentially useful modality in ruling out testicular torsion because it is noninvasive, portable, easily accessible for bedside use, and easy to interpret. Laboratory tests are unlikely to be of consequence, as no single test has high sensitivity or specificity in diagnosing testicular torsion. . Bhatt S, Rubens DJ. Sonographic Evaluation of Testicular Torsion. Ultrasound Clinics. 2006. 1:55-66. Yagil Y, Naroditsky I, Milhem J, Leiba R, Leiderman M, Badaan S, et al. Role of Doppler .
Keywords: testicular torsion, color doppler ultrasound. Trauma aside, torsion of the appendix testis, acute epididymitis, orchitis, testicular tumor, incarcerated inguinal hernia, and Henoch–Schönlein purpura are some of the conditions that may present as an acute scrotum. . CDUS is the most effective and convenient test in diagnosing . Purpose Testicular torsion requires emergency surgery; thus, prompt and correct diagnosis is very important. Ultrasound with color Doppler is usually the first-choice modality for diagnosis; however, skill and experience are required for confident diagnosis. Recently, contrast-enhanced ultrasound for the diagnosis of testicular torsion has been reported, but there .
Consider the diagnosis of testicular torsion in all patients with acute testicular pain; Testicular torsion is a surgical emergency that requires immediate urologic consultation to increase the rate of tissue salvage. History, physical examination and ultrasound are all flawed in making the diagnosis. The gold standard is surgical explorationTesticular torsion is a result of the twisting of the testis and spermatic cord within the scrotum, with resultant occlusion of venous return and edema. If the torsion persists, it can lead to arterial occlusion and ischemia. . Ultrasound is the test of choice in the emergency department to diagnose torsion when the clinical diagnosis is not .
Purpose Our aim was to determine the accuracy of ultrasound (US) examination-based testicular torsion diagnosis in adult patients with acute scrotal pain. Methods A comprehensive electronic search was performed using internet retrieval systems up to 5 August 2018 in accordance with the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta . Acute scrotal pain makes up approximately 0.5% of all emergency department complaints. 1 History and physical examination can be relatively non-specific, resulting in a broad differential diagnosis of potential etiologies. Among these, testicular torsion is the most important and time-sensitive diagnosis to make.Testicular torsion occurs when the spermatic cord (from which the testicle is suspended) twists, cutting off the blood supply to the testicle. [3] The most common symptom in children is sudden, severe testicular pain. [1] The testicle may be higher than usual in the scrotum and vomiting may occur. [1] [2] In newborns, pain is often absent and instead the scrotum may become .
Ultrasound. This imaging test uses sound waves to create pictures of your testicles. The test can show if you have testicular torsion. Testicular torsion is a twisting of the testicle that can cut off blood flow. If ultrasound with color Doppler shows lower blood flow to a testicle than is typical, the testicle is twisted. .
Testicular torsion is a medical emergency that requires an immediate and multidisciplinary approach from emergency, surgical, and radiological services. In this article, we discuss the current knowledge and growing value of ultrasound (US) for intravaginal testicular torsion diagnosis and our experience with manual testicular detorsion with US assistance. . Scrotal exploration should be considered in the presence of high clinical suspicion for testicular torsion, even if the ultrasound findings are nonspecific. References. Zhao LC, Lautz TB, Meeks JJ, Maizels M. Pediatric .
Because extrinsic compression of the testicular parenchyma or spermatic cord can compromise inflow and outflow, one should evaluate for fluid collections around the testis and pathologic findings along the inguinal canal, .Test Overview. A testicular ultrasound (sonogram) is a test that uses reflected sound waves to show a picture of the testicles and scrotum.The test can show the long, tightly coiled tube that lies behind each testicle and collects sperm (epididymis). And it can show the tube (vas deferens) that connects the testicles to the prostate gland.The ultrasound does not use X-rays or other .
Testicular torsion is a twisting of the spermatic cord and its contents and is a surgical emergency affecting 3.8 per 100,000 males younger than 18 years annually. It accounts for 10% to 15% of Sonographic Evaluation of Testicular Torsion. Ultrasound Clinics. 2006. 1:55-66. Yagil Y, Naroditsky I, Milhem J, Leiba R, Leiderman M, Badaan S, et al. Role of Doppler ultrasonography in the triage of acute scrotum in the emergency department. . Menon VS, et al. Transscrotal Near Infrared Spectroscopy as a Diagnostic Test for Testis Torsion .Testicular ultrasound is done to: Check a mass or pain in the testicles. Find or check on an infection or swelling of the testicles or epididymis. Check for twisting of the spermatic cord. This problem cuts off blood supply to the testicles (testicular torsion). Check to see if testicular cancer has come back. Find an undescended testicle.
A testicular ultrasound (sonogram) is a test that uses reflected sound waves to show a picture of the testicles and scrotum. The test can show the long, tightly coiled tube that lies behind each testicle and collects sperm (epididymis). . This twisting (testicular torsion) cuts off blood supply to the testicles. There is no sign of fluid in . In the United States, approximately 96% of groin hernias are inguinal hernias, about 20% of which are bilateral. 1 Femoral hernias comprise the remaining 4% of groin hernias and are more common in . There are several signs of testicular torsion on scrotal ultrasound. Starting from the superior aspect, the spermatic cord can be seen with a whirlpool sign (knot-like) when compared to the unaffected side. . Arterial waveform resistive index (RI) is one of the most sensitive and specific tests for testicular torsion. The RI is calculated .
In a study of 236 patients with a clinical suspicion of testicular torsion, color-coded Doppler ultrasound had a sensitivity and specificity of 100% and 75.2%, and positive and negative predictive values of 80.4% and 100%, respectively. 5 This strong negative predicative value makes color-coded Doppler ultrasonography the ideal test to rule out . The Testicular Workup for Ischemia and Suspected Torsion (TWIST) score is a clinical decision tool used for the workup and management of acute scrotal emergencies where testicular torsion is suspected. It uses history and examination to estimate the likelihood of torsion. Validation of the clinical score has only been conducted in the pediatric population.
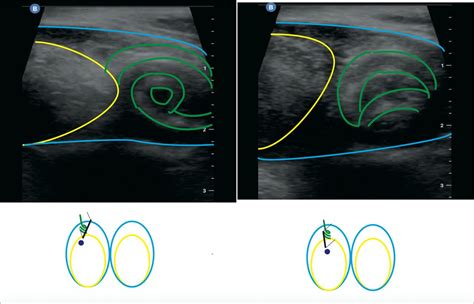
whirlpool sign testicular ultrasound
whirlpool sign testicular torsion ultrasound
Resultado da Prepare-se para enfrentar o frio com conforto e estilo com a nossa Bota feita especialmente para essa estação! Nossa bota foi especialmente projetada .
test for testicular torsion ultrasound|testicular torsion treatment guidelines